02.28.2022 UPDATE: The Food and Drug Administration is expanding its advisory on powdered baby formulas to include a certain lot of specialty Similac PM 60/40 manufactured in Sturgis, Michigan. This is in addition to lots of Similac®, Alimentum® and EleCare® powder formula that were voluntarily recalled on Feb. 17.
On Feb. 28, CDC announced one additional illness of Cronobacter sakazakii with exposure to powdered infant formula produced at Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, Michigan facility. Cronobacter infection may have been a contributing cause of death for this patient.
The most recent patient was reported to have consumed Abbott Nutrition’s Similac PM 60/40 product with the lot code 27032K800 prior to Cronobacter sakazakiiI infection. The FDA and CDC informed the firm of these findings and on Feb. 28, 2022, Abbott Nutrition voluntarily recalled Similac PM 60/40 powdered infant formula with the lot code 27032K800. This is a specialty formula for certain infants who would benefit from lowered mineral intake and was not included in the previous recall. At this time, Similac PM 60/40 with lot code 27032K80 (can) / 27032K800 (case) are the only type and lots of this specialty formula being recalled.
To check if your powdered formula is part of the recall, enter the product lot code on the bottom of your package on Abbot Nutrition’s recall website.
For more information about the recall, or to ask questions, get assistance from the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN).
If your infant is experiencing symptoms related to Cronobacter or Salmonella infection, such as poor feeding, irritability, temperature changes, jaundice, grunting breaths, abnormal movements, lethargy, rash, or blood in the urine or stool; contact your health care provider to report their symptoms and receive immediate care.
To report an illness or adverse event to the FDA, you can
-
- Call an FDA Consumer Complaint Coordinator if you wish to speak directly to a person about your problem.
- Complete an electronic Voluntary MedWatch form online.
- Complete a paper Voluntary MedWatch form that can be mailed to FDA.
The FDA, along with CDC and state and local partners, are investigating four consumer complaints of infant illness related to products from Abbott Nutrition. All of the cases are reported to have consumed powdered infant formula (IF) produced from Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, MI facility. These complaints, received from 9/20/2021 to 1/11/2022, include three reports of Cronobacter sakazakii infections and one report of Salmonella Newport infection in infants. All four cases related to these complaints were hospitalized, and Cronobacter may have contributed to a death in one case.
FDA has initiated an onsite inspection at the facility. Findings to date include several positive Cronobacter results from environmental samples taken by FDA, and adverse inspectional observations by FDA investigators. A review of the firm’s internal records also indicate environmental contamination with Cronobacter sakazakii and the firm’s destruction of product due to the presence of Cronobacter.
FDA is issuing this advisory to alert consumers to avoid purchasing or using recalled powdered infant formula produced in the Sturgis, MI facility.
On 2/17/2022, Abbott Nutrition initiated a voluntary recall of certain powdered infant formulas. Products made at the Sturgis facility can be found across the United States and were likely exported to other countries as well. Canadian health officials have also issued a recall warning. FDA is continuing to investigate and will update this advisory should additional consumer safety information become available.
Recommendation
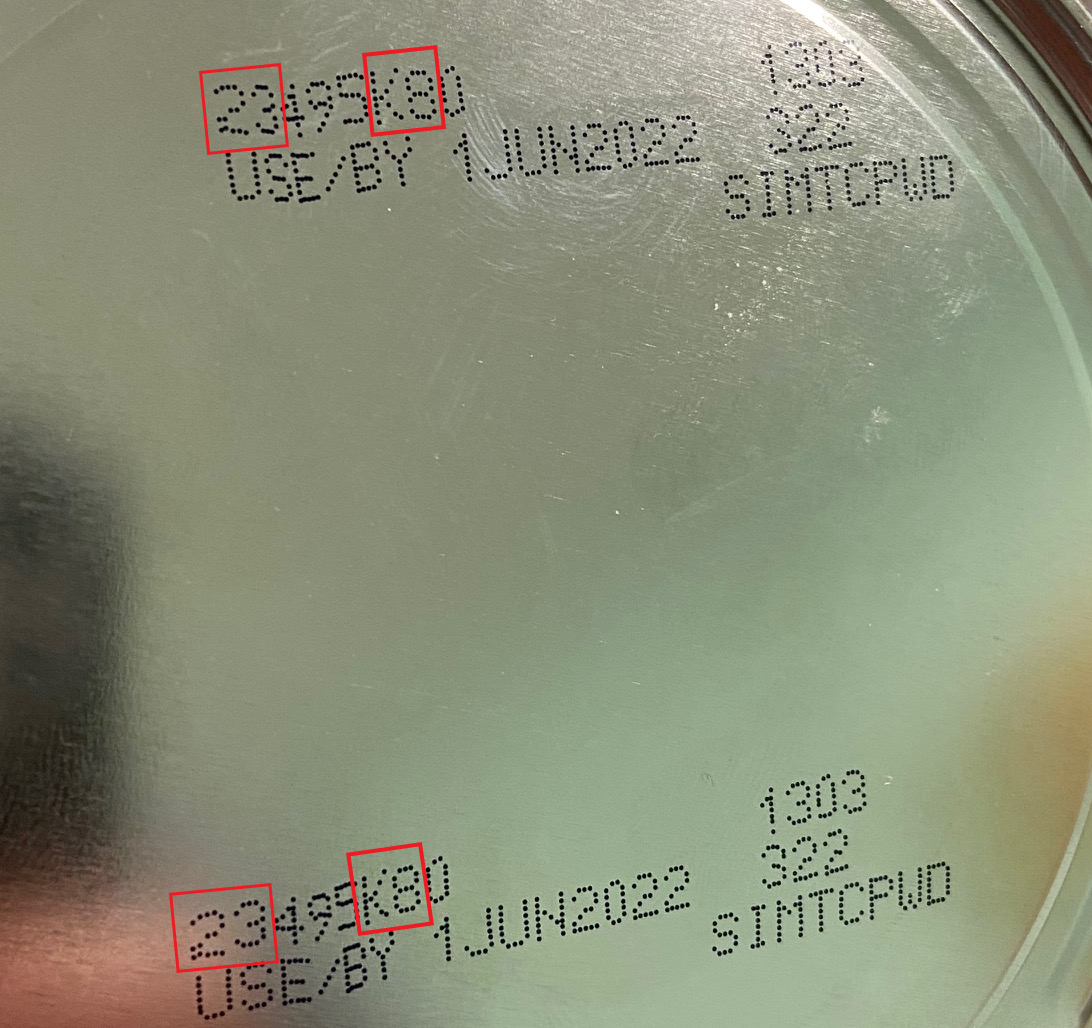
The FDA is advising consumers not to use recalled Similac, Alimentum, or EleCare powdered infant formulas. Recalled products can be identified by the 7 to 9 digit code and expiration date on the bottom of the package (see image below). Products are included in the recall if they have all three items below:
- the first two digits of the code are 22 through 37 and
- the code on the container contains K8, SH, or Z2, and
- the expiration date is 4-1-2022 (APR 2022) or later.
Additional recall information is available on the FDA website. Parents can also enter their product lot code on the company’s website to check if it is part of the recall.
Additional Information for Parents and Caregivers:
The recall does not include liquid formula products or any metabolic deficiency nutrition formulas. Consumers should continue to use all product not included in the recall.
Parents and caregivers should never dilute infant formula and should not make or feed homemade infant formula to infants. Consumers should also avoid purchasing imported formula through online sales, as it has the potential to be counterfeit.
If your regular formula is not available, contact your child’s healthcare provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices.
More information on Cronobacter and infant formula is available on CDC’s website.
Recalled powdered infant formulas have the potential to be contaminated with Cronobacter, a bacterium that can cause severe foodborne illness primarily in infants. Cronobacter infections are rare but are especially high risk for newborn infants (see symptoms below).
Cronobacter bacteria can cause severe, life-threatening infections (sepsis) or meningitis (an inflammation of the membranes that protect the brain and spine). Symptoms of sepsis and meningitis may include poor feeding, irritability, temperature changes, jaundice (yellow skin and whites of the eyes), grunting breaths, and abnormal movements. Cronobacter infection may also cause bowel damage and may spread through the blood to other parts of the body.
If your child is experiencing any of these symptoms, you should notify your child’s healthcare provider and seek medical care for your child immediately. Healthcare providers and health departments are encouraged to report any confirmed cases of Cronobacter sakazakii to CDC.

Case Counts
Total Adverse Events: 4 (3 Cronobacter, 1 Salmonella)
Hospitalizations: 4
Reported Deaths: 1*
Adverse Event Dates: 9/6/2021 – 12/18/2021
States with Adverse Events: MN (1), OH (1), TX (2)
Product Distribution: Nationwide and International
*One death has been reported but has not been confirmed to be solely attributable to Cronobacter infection.