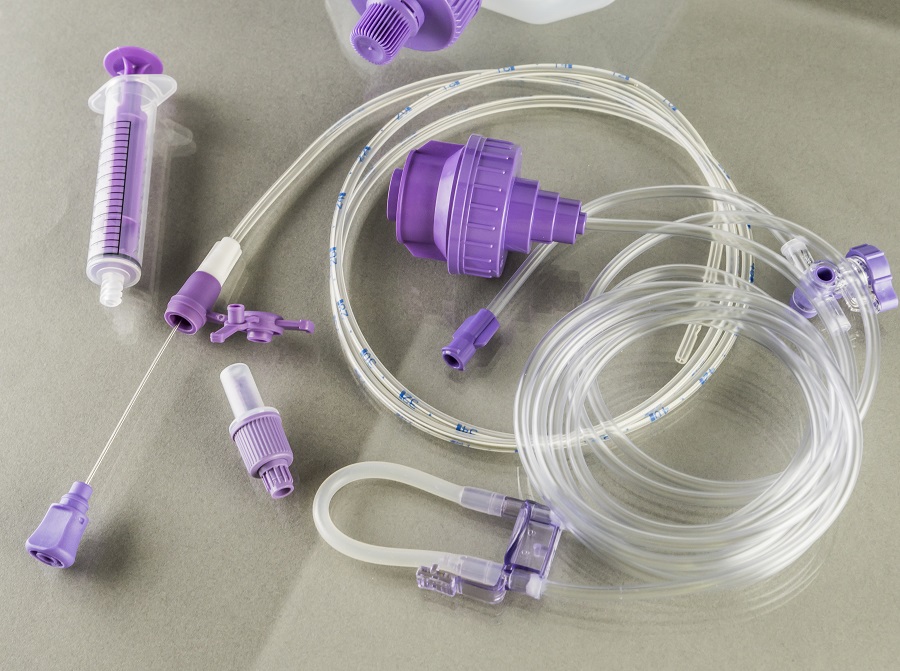
Enteral misconnections occur when enteral devices, or feeding tubes are accidentally connected to non-ENFit devices, such as IV lines, respiratory tubing or urinary devices.
The FDA has received reports of 2 deaths and 24 serious injuries related to enteral misconnections just since 2011. It is thought that many enteral misconnections do not get reported to the FDA.
Several organizations, including the FDA, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), The Joint Commission and enteral device manufacturers agreed on an enteral connection design that is compatible only with enteral devices. It is physically incompatible with IV, respiratory, urinary and other types of non-enteral devices. The connection design is called ISO 80369-3, more commonly known by the brand name, ENFit.
Although more than 80 California hospitals have transitioned to use of ENFit connectors for enteral devices, fewer hospitals have adopted the standard across the rest of the US. Many are in the planning stages, realizing that full adoption is a tedious process and may take several months. Find resources to help hospitals plan for and adopt ENFit here: http://stayconnected.org/tools-adopting-enfit/
On September 7, 2018 the FDA released a letter to manufacturers, healthcare professionals and hospital purchasing departments encouraging the use of 80369-3 or ENFit connectors in order to reduce risk of misconnection and patient injury. They provided the following recommendations.
Recommendations for Manufacturers:
- Design safe enteral device connectors that are not compatible with non-enteral devices.
- Consider patient safety when designing enteral devices.
- Comply with design standard ISO 80369-3/ENFit connectors to reduce risk of misconnection.
- Plan to eventually stop producing legacy devices (enteral devices that are still compatible with non-enteral devices).
Recommendations for Health Care Professionals:
- Use safe enteral devices that comply with ISO 80369-3/ENFit in order to reduce risk of enteral misconnections.
- Check with manufacturers to ensure that your enteral connectors meet ISO 80369-3/ENFit standards.
- Develop a plan to implement ISO 80369-3/ENFit-compliant safe enteral devices in your facility.
- Avoid modifications or the use of adaptors that defeat the purpose of safe enteral devices.
- Minimize use of transition adaptors – although they may be necessary during transition to safe enteral devices, they are a short term solution and defeat the purpose of safe enteral devices.
- Trace all lines to their origin before connecting any devices.
Recommendations for Hospital Purchasing Departments and Distributors:
- Purchase enteral devices that comply with ISO 80369-3/ENFit standards to reduce risk of misconnection.
- Ensure that adequate inventory of ISO 80369-3/ENFit-compliant devices is available for purchase.
Reference:
Letter to Manufacturers of Enteral Feeding Tubes, Health Care Professionals, and Hospital Purchasing Departments and Distributors: The FDA Encourages Use of Enteral Device Connectors that Reduce Risk of Misconnection and Patient Injury – September 7, 2018
FDA Activities: Medical Device Connectors
ENFit® is a federally registered trademark of GEDSA.
Used with permission.
For More Articles on Enteral Misconnections and ENFit: