What are Essential Fatty Acids?
The human body can make most of the fats it needs through our diet. However, there are two fatty acids that are essential, meaning we must consume them through our diet because the body alone cannot synthesize them. These are Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
What is an Omega-3 Fatty Acid?
There are three different types of Omega-3 fatty acids: EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Omega-3 fatty acids have several important roles in the body. They are needed for cell growth and repair; they are important for brain function; and most importantly, they are associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, which is currently the leading cause of death in the United States. Recent evidence also shows that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce the inflammation associated with obesity.
What is an Omega-6 Fatty Acid?
Most Omega-6 fatty acids come in the form of LA (Linoleic Acid), which supports a wide variety of physiologic functions in the body, including: stimulating hair and skin growth; aiding in cell division, repair and growth; and regulating brain function. Although Omega-6 fatty acids are critical for many bodily functions, the most important thing is that we are consuming these fatty acids in the right amount! Too much Omega-6’s in our diet can promote inflammation in the body.
| Omega-3 | Omega-6 |
| Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Tuna, Sardines, Oysters) Vegetable Oils (soybean, walnut, flaxseed, canola) Green Veggies (Spinach, Kale, Brussel Sprouts) Chia Seeds |
Most Vegetable Oils (safflower, sunflower) Processed Foods (cookies, crackers, sweets) Margarine Nuts Seeds |
What is the Issue?
The standard American diet provides almost 10 times more omega-6 than omega-3 fatty acids. The average ratio of consumption of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids is from 10:1-20:1, and in some individuals as high as 25:1.
There is now scientific agreement that we should consume MORE omega-3 fatty acids and LESS omega-6 fatty acids for better health. The imbalance of these fatty acids can contribute to an increased risk of chronic disease. Improving this balance is now a valuable approach to achieving optimal health. The American diet needs to include more omega-3 rich foods to reduce the omega-6:omega-3 ratio, which will promote better health.
Aim for getting 8 ounces of seafood consumption per week. You may also want to discuss with your doctor if supplementing with fish oil is a good option for you.
Incorporating More Omega 3’s
- Add spinach and ground flaxseeds to morning blended protein shake or smoothie
- Designate one night per week to eating seafood
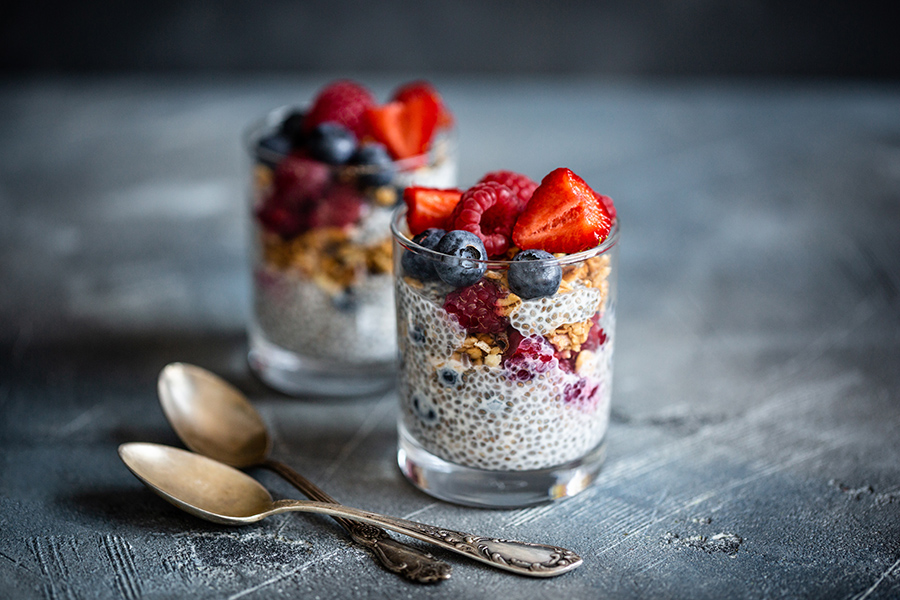
- Try a chia seed pudding with breakfast (recipe below)
Chia Seed Pudding Recipe (2 servings)
Ingredients:
- 1 cup unsweetened vanilla almond milk (any milk alternative is fine)
- ¼ cup chia seeds
- Sweetener to taste (agave nectar, stevia, etc)
Directions:
- In a bowl, mix together chia seeds and milk. Cover and let sit in refrigerator overnight.
- Top with blueberries, strawberries or your favorite nuts.
- If desired, drizzle on some agave nectar or sweetener of your choice.